The Internet Protocol Suite (commonly known as TCP/IP) is the set of communications protocols used for the Internet and other similar networks. It is named from two of the most important protocols in it: the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP), which were the first two networking protocols defined in this standard. Today's IP networking represents a synthesis of several developments that began to evolve in the 1960s and 1970s, namely the Internet and LANs (Local Area Networks), which emerged in the mid- to late-1980s, together with the advent of the World Wide Web in the early 1990s.
The Internet Protocol Suite, like many protocol suites, may be viewed as a set of layers. Each layer solves a set of problems involving the transmission of data, and provides a well-defined service to the upper layer protocols based on using services from some lower layers. Upper layers are logically closer to the user and deal with more abstract data, relying on lower layer protocols to translate data into forms that can eventually be physically transmitted.
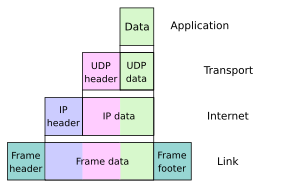
The TCP/IP model consists of four layers (RFC 1122).[1][2] From lowest to highest, these are the Link Layer, the Internet Layer, the Transport Layer, and the Application Layer.
History
The Internet Protocol Suite resulted from research and development conducted by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) in the early 1970s. After initiating the pioneering ARPANET in 1969, DARPA started work on a number of other data transmission technologies. In 1972, Robert E. Kahn joined the DARPA Information Processing Technology Office, where he worked on both satellite packet networks and ground-based radio packet networks, and recognized the value of being able to communicate across both. In the spring of 1973, Vinton Cerf, the developer of the existing ARPANET Network Control Program (NCP) protocol, joined Kahn to work on open-architecture interconnection models with the goal of designing the next protocol generation for the ARPANET.
By the summer of 1973, Kahn and Cerf had worked out a fundamental reformulation, where the differences between network protocols were hidden by using a common internetwork protocol, and, instead of the network being responsible for reliability, as in the ARPANET, the hosts became responsible. Cerf credits Hubert Zimmerman and Louis Pouzin, designer of the CYCLADES network, with important influences on this design.
The design of the network included the recognition that it should provide only the functions of efficiently transmitting and routing traffic between end nodes and that all other intelligence should be located at the edge of the network, in the end nodes. Using a simple design, it became possible to connect almost any network to the ARPANET, irrespective of their local characteristics, thereby solving Kahn's initial problem. One popular saying has it that TCP/IP, the eventual product of Cerf and Kahn's work, will run over "two tin cans and a string."
A computer called a router (a name changed from gateway to avoid confusion with other types of gateways) is provided with an interface to each network, and forwards packets back and forth between them. Requirements for routers are defined in (Request for Comments 1812).[3]
The idea was worked out in more detailed form by Cerf's networking research group at Stanford in the 1973–74 period, resulting in the first TCP specification (Request for Comments 675) [4]. (The early networking work at Xerox PARC, which produced the PARC Universal Packet protocol suite, much of which existed around the same period of time, was also a significant technical influence; people moved between the two.)
DARPA then contracted with BBN Technologies, Stanford University, and the University College London to develop operational versions of the protocol on different hardware platforms. Four versions were developed: TCP v1, TCP v2, a split into TCP v3 and IP v3 in the spring of 1978, and then stability with TCP/IP v4 — the standard protocol still in use on the Internet today.
In 1975, a two-network TCP/IP communications test was performed between Stanford and University College London (UCL). In November, 1977, a three-network TCP/IP test was conducted between sites in the US, UK, and Norway. Several other TCP/IP prototypes were developed at multiple research centres between 1978 and 1983. The migration of the ARPANET to TCP/IP was officially completed on January 1, 1983, when the new protocols were permanently activated.[5]
In March 1982, the US Department of Defense declared TCP/IP as the standard for all military computer networking.[6] In 1985, the Internet Architecture Board held a three day workshop on TCP/IP for the computer industry, attended by 250 vendor representatives, promoting the protocol and leading to its increasing commercial use.
Layers in the Internet Protocol Suite
The concept of layers
The TCP/IP suite uses encapsulation to provide abstraction of protocols and services. Such encapsulation usually is aligned with the division of the protocol suite into layers of general functionality. In general, an application (the highest level of the model) uses a set of protocols to send its data down the layers, being further encapsulated at each level.
This may be illustrated by an example network scenario, in which two Internet host computers communicate across local network boundaries constituted by their internetworking gateways (routers).
The functional groups of protocols and methods are the Application Layer, the Transport Layer, the Internet Layer, and the Link Layer (RFC 1122). It should be noted that this model was not intended to be a rigid reference model into which new protocols have to fit in order to be accepted as a standard.
The following table provides some examples of the protocols grouped in their respective layers.
| Application | DNS, TFTP, TLS/SSL, FTP, Gopher, HTTP, IMAP, IRC, NNTP, POP3, SIP, SMTP,SMPP, SNMP, SSH, Telnet, Echo, RTP, PNRP, rlogin, ENRP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Routing protocols like BGP and RIP which run over TCP/UDP, may also be considered part of the Internet Layer. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport | TCP, UDP, DCCP, SCTP, IL, RUDP, RSVP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Internet | IP (IPv4, IPv6), ICMP, IGMP, and ICMPv6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OSPF for IPv4 was initially considered IP layer protocol since it runs per IP-subnet, but has been placed on the Link since RFC 2740. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ARP, RARP, OSPF (IPv4/IPv6), IS-IS, NDPLayer names and number of layers in the literatureThe following table shows the layer names and the number of layers of networking models presented in RFCs and textbooks in widespread use in today's university computer networking courses.
These textbooks are secondary sources that may contravene the intent of RFC 1122 and other IETF primary sources[18]. Different authors have interpreted the RFCs differently regarding the question whether the Link Layer (and the TCP/IP model) covers Physical Layer issues, or if a hardware layer is assumed below the Link Layer. Some authors have tried to use other names for the Link Layer, such as network interface layer, in view to avoid confusion with the Data Link Layer of the seven layer OSI model. Others have attempted to map the Internet Protocol model onto the OSI Model. The mapping often results in a model with five layers where the Link Layer is split into a Data Link Layer on top of a Physical Layer. In literature with a bottom-up approach to Internet communication[10][11][13], in which hardware issues are emphasized, those are often discussed in terms of Physical Layer and Data Link Layer. The Internet Layer is usually directly mapped into the OSI Model's Network Layer, a more general concept of network functionality. The Transport Layer of the TCP/IP model, sometimes also described as the host-to-host layer, is mapped to OSI Layer 4 (Transport Layer), sometimes also including aspects of OSI Layer 5 (Session Layer) functionality. OSI's Application Layer, Presentation Layer, and the remaining functionality of the Session Layer are collapsed into TCP/IP's Application Layer. The argument is that these OSI layers do usually not exist as separate processes and protocols in Internet applications.[citation needed] However, the Internet protocol stack has never been altered by the Internet Engineering Task Force from the four layers defined in RFC 1122. The IETF makes no effort to follow the OSI model although RFCs sometimes refer to it. The IETF has repeatedly stated[citation needed] that Internet protocol and architecture development is not intended to be OSI-compliant. RFC 3439, addressing Internet architecture, contains a section entitled: "Layering Considered Harmful". NetworksMost people working in office with more than a couple of computers will be using some form of network. As networks become easier to setup and maintain more home users are also setting up networks to share resource such as disk space, printers, Internet connections and access to software. A network is basically two or more computers connected through a cable or wire which share resources. Network software controls how the computers communicate. There are dozens of different types of networks which are impossible to cover in an introduction article. This article focuses on home and small business networks using some version of the Window operating system. To connect computers each of the computers needs a network card with a connection that allows a cable to be connected to it. Computers can be connected directly through a bi-directional cable or through an other piece of hardware called a hub. The hub then connects all the computers in your local network together. Both solutions cost about the same but a hub allows more than two computers to connect. A hub can also be used to connect two local area networks together to create a wide area network. Some form of network software is required. This network protocol software is installed through the network preferences. NetBIOS was commonly used though recently a secure TCP/IP protocol has been developed. The network protocol determines how computers become part of the network and how they are recognized. The network must have a name and you can use some creativity at this point. Each computer must also have a unique name that other computers on the network can access them with. If all goes well this is all you need but often there will be a conflict that can be resolved by establishing exactly how the computer will communicate. To solve these types of conflict your network needs a set DNS server address and each computer in the network needs to be assigned a unique IP address. The addresses usually are in the range of 192.168.x.x where x means any number between 0 and 255. Once these numbers have been entered your network should be functioning with each computer able to see the other computers on the network. You must also decide which resources you want to share. You may want to make a disk or folder available, a printer or tape backup system so that everyone can use it. You may also want to have parts of the network that are either not accessible or accessible only through a password. File and print sharing must be enable on the computer that will share it's resources or host computer and they determine how they are accessed by other computers or clients. A computer with an Internet connection can also share that connection with other computers on the network but you should check with your ISP what their policy on sharing Internet connections is. Sharing an Internet connection also raises some serious security issues. Many cable high speed Internet connections use the Network Neighborhood settings to create the Internet connection and connecting your home or office network to this existing system can cause problems. Though you may want to allow a computer in another room of the house to access files or run programs on your computer you probably don't want the kid down the block to have that same access. Security on networks begin with passwords. Everyone who wishes to access the network must logon with a username and password. If someone cancels the password challenge they will be able to access the files and programs on that individual computer but can't access any of the network resources. Specific passwords for important folders or disks can also be set or access to folders or disks can be forbidden. Unlike server/client networks where the server must be running before the computers can communicate the peer-to-peer network that comes packaged with Windows allow any computers that are turned on to communicate with other. Other computers in the network become accessible as user turn them on. Networks can also be open to remote secure access through a virtual private network. A VPN allows a computer to connect to a computer or network through the Internet. |

No comments:
Post a Comment